Categories
Tags
-
#heat pump
#Coconut shell activated carbon
#Columnar activated carbon
#Honeycomb activatedcarbon
#Ceramic Foam Filter Casting Filtration
#Alumina Ceramic Foam Filter for Aluminium
#ceramic foam filter
#Casting tip
#Ceramic foam filters
#Foundry Ceramic Foam Filters
#Air Handling Unit
#air heat pump cost
#cooling tower
#cross flow cooling tower
#snookball
#Snookball Table
Archives
HONMING cross flow cooling tower
-
Principle
In cross flow cooling tower, water is falling from above, the air and water are flow in vertical way. Because heat dissipation material is closed to the collection basin, the advantage is reducing water falling noise. Cross flow type usually used in square cooling tower, but the structure is fixed with large amount of iron piece, so it cost higher than round cooling tower.
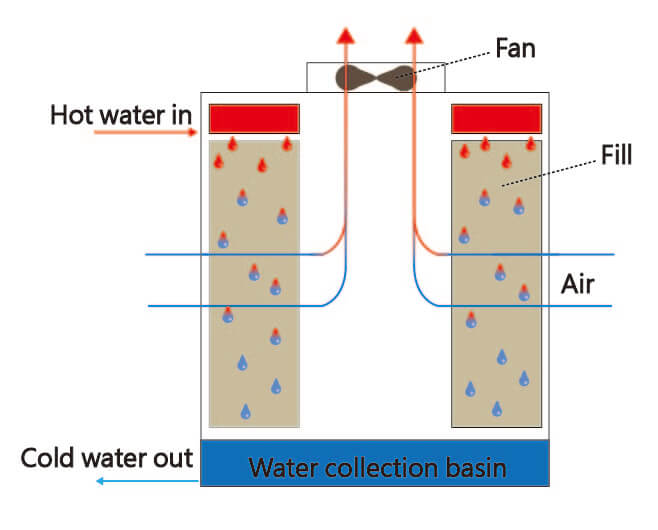
Characteristic
- Simple design.
- Easy maintenance.
- Low noise of water pressure.
- Smaller floor space, more economic benefits for long term use.
Counter flow cooling tower
Principle
In counter flow cooling tower, cooling air and water flow are in opposite direction, for this reason, it can reach maximum area of dissipation. It commonly used in round cooling tower, and also used in square cooling tower in some case.
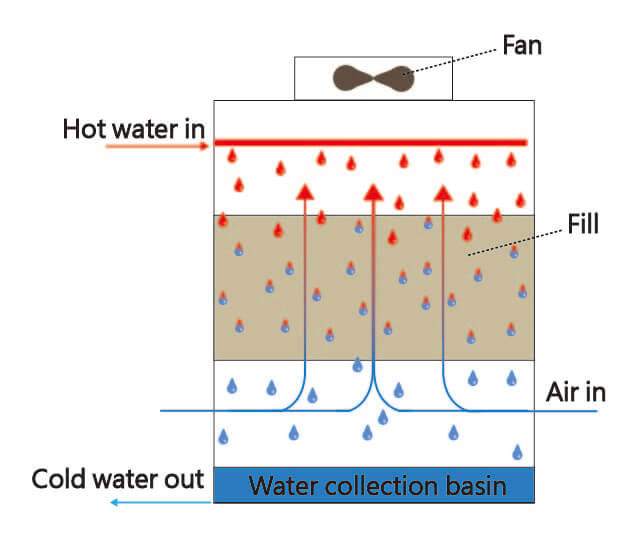
Characteristic
- High efficiency of heat exchange.
- Inside structure complicated, difficult to maintenance.
- Easy to produced limescale and moss.
- Fills of round cooling tower can’t be maintenance regularly.
- It’s easier to occurs splash drift losses problem.
Advantage of HONMING Closed Circuit Cooling Tower
- Overcome limescale problem.
- #304 stainless steel shell and coil (zinc aluminum-plate available).
- Air/water flow in the same way, and cross type design.
- Low splash drift losses.
- Large maintenance space.
- Natural Draft Cooling Towers
As their name implies, natural draft cooling towers rely on natural convection to circulate air throughout the tower, which then cools the water. Air movement occurs due to differences in density between the entering air and the internal air within the tower. Warm, moist air, which is denser than cool air, will naturally rise through the tower, while the dry, cool air from outside will fall, creating a constant cycle of airflow.
- Mechanical Draft Cooling Towers
Unlike natural draft cooling towers, mechanical draft cooling towers employ fans or other mechanics to circulate air through the tower. Common fans used in these towers include propeller fans and centrifugal fans. Mechanical draft towers are more effective than natural draft towers, and can even be located inside a building with the proper exhaust system. However, they consume more power than natural draft cooling towers and cost more to operate as a result.
Types of Mechanical Draft Cooling Towers
There are two types of mechanical draft cooling towers:
A. Crossflow Towers
In a crossflow tower, air flows horizontally through the cooling tower’s structure while hot water flows downward from distribution basins. Crossflow towers can be as tall as counterflow towers, but they’re also more prone to freezing and are less efficient.
B. Counterflow Cooling Towers
This type of cooling tower moves air upward through the tower while water flows downward to cool the air. These towers are often more compact in footprint than crossflow towers and can save energy in the long run.
Cooling Tower Build Type
Cooling towers can differ by build as well as heat transfer and air generation methods. When it comes to cooling tower build, there is the:
- Package type. These are small, compact, and pre-fabricated cooling towers used for smaller industries, such as hospitals or schools. These are factory-fabricated and shipped on trucks.
- Field erection type. These are large, specified units used for power plants and other larger industrial factories. These are fabricated on-site and are larger than a typical house.